Measurable results with sacral nerve testing
Move one step closer to identifying if sacral nerve damage is associated with your patients symptoms.
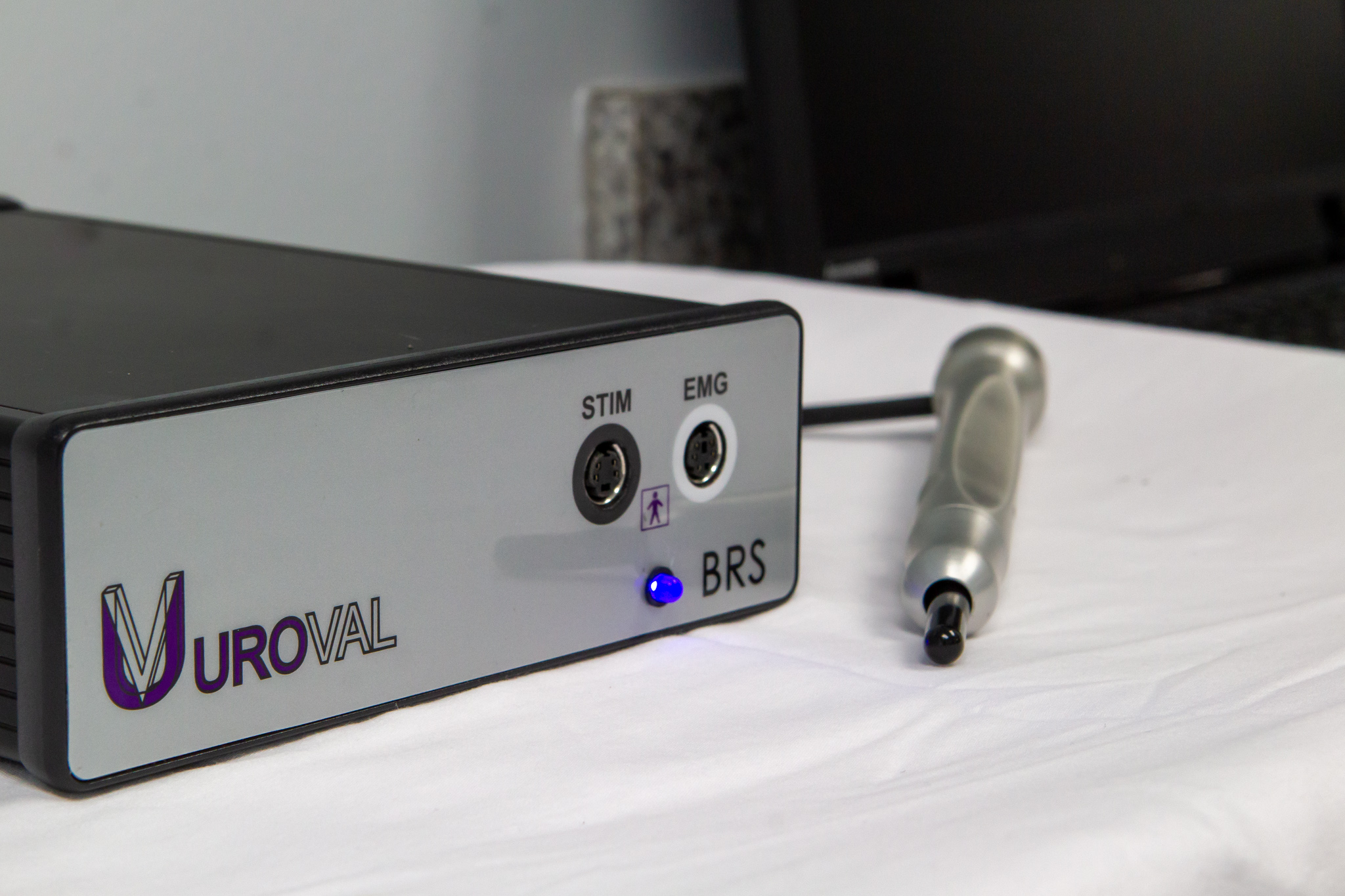
Make UroVal’s Bulbocavernosus Reflex System
Your Standard of Care
“Clinical assessment of the Bulbocavernosus reflex(BCR) should be as essential a part of the routine urologic assessment of patients with voiding disturbances as a knee jerk is for routine neurologic examination.”¹
With UroVal’s® Bulbocavernosus Reflex System, you do more than establish the presence of bulbocavernosus reflex. Objectively measure the time between stimulus and reflex, establish if the patient’s reflex is within normal limits, and get one step closer to identifying if nerve damage is the underlying cause of your patient’s condition. In minutes, get the data you need on demand with no electrical stimulation and no anal insertion.
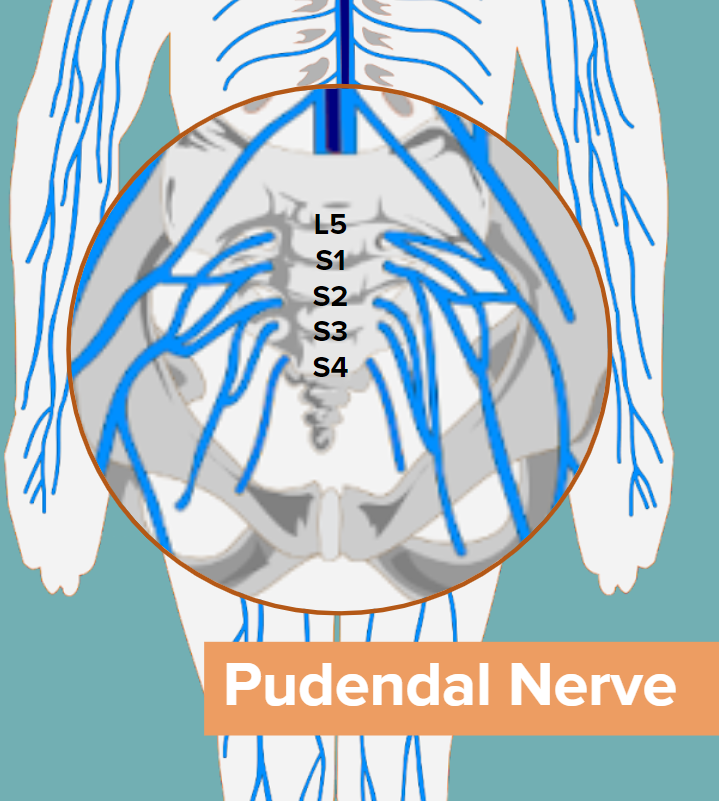
What is BCR?
The Bulbocavernosus reflex is an indicator of sacral nerve function. The clinical standard for evaluating the BCR is a manual exam that consists of inserting a finger into the anus, and then squeezing the genitalia in order to elicit the anal wink.² The results of this manual technique are limited to determining the presence or absence of the reflex.
Other currently available techniques that provide measurable BCR results include electromyographic testing that involves electrical stimulation and inserting a finger into the external anal sphincter. UroVal does not require electrical stimulation or any anal insertion.
Use UroVal BRS to:
- Evaluate nerve damage in urinary incontinence and sacral nerve dysfunction
- Establish a baseline nerve function before, during, and after treatment
- Utilize the BRS to assist with choices in treatment plans
Treatment Decision Examples
Urinary Incontinence
In patients whose BCR latency is prolonged (implying nerve damage), medications may not work well and a stimulation of pelvic floor rehab option for treatment has been documented to show greater effectiveness. ²,³
UroVal’s BRS
- Can be performed by ancillary medical personnel**
- Mechanical tap is the stimulus
- No Bodily Insertion
- No electrical stimulation
- Usually a few minutes to complete
- Latency measured in milliseconds
- Can be performed by ancillary medical personnel**
- Mechanical tap is the stimulus
- Objective report with graph
- No bodily insertion
- No electrical stimulation
- Usually a few minutes to complete
Reimbursement
- Average CMS allowable nationwide is $277.60
- Billing support is available from our billing consultant and is available to provide counseling tailored to your practice.
- Assistance with any denials.
Average Medicare Allowable*
$277.60
UNDERSTAND: This information was retrieved from http://www.cms.hhs.gov/apps/
Our team
We are ready to serve you

Brad Cole
Managing Director & EVP of Sales, Chairman of Vijuvia Life Centers LLC
Your Title Goes Here
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Your Title Goes Here
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

Marcus McGehee
Digital Marketing Coordinator

Dave Walker
Chief Operations Officer

Amy Dittmar
Director of Customer Service
Ready To Get Started?
Fill out the form to have one of our sales representatives get in touch.
“Our practice at UNLV medicine has utilized the BR latency evaluation procedure for more than 4 years and have found it to be an exceptional and fundamental piece of information in determining patient diagnosis and best treatment options.”¹
Adam V. Levy, MD Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, UNLV
Citation:¹(J.Blaivas, A. Zayed, K.Labib, 1981)
2 Devine, Evangelidis, Hall”Bulbocavernosus Reflex: Does it have a role in the treatment of
detrusor instability?”
3 Levy, Bradley, Prachi, Cross:”Use of Bulbocavernosus Reflex directed pelvic floor
rehabilitation for treatment of urinary incontinence as an objective measure of treatment
effectiveness”
4 Direct Supervision §§ 410.32 (b) (ii)
5 www.cms.gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/overview.aspx.
² Granata G, Padua L, Rossi F, De Franco P, Coraci D, Rossi V. Electrophysiological study of the bulbocavernosus reflex: normative data. Funct Neurol. 2013;28(4):293-295. doi:10.11138/FNeur/2013.28.4.293